https://ravjot.hashnode.dev/what-the-heck-is-zero-knowledge-zk-proof
[](data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB3aWR0aD0iMTYwMCIgaGVpZ2h0PSI4NDAiIHhtbG5zPSJodHRwOi8vd3d3LnczLm9yZy8yMDAwL3N2ZyIgdmVyc2lvbj0iMS4xIi8+)
So you have heard it, ZK proofs or Zero Knowledge proofs. But why there is a sudden buzz? What is it? What are zk-rollups? What are ZK-SNARKs? All of your questions will be answered so hang tight and ride along!
A method by which one party (Prover) can prove that it knows a secret or a statement is true to another party(Verifier) without revealing any actual information.
The term "Zero Knowledge" in itself it the testimony to the fact that no information is revealed but the second party (Verifier) is rightfully convinced that first party (Prover) knows the secret or their statement is true.
So why would we need Zero Knowledge proof? When we don't trust someone with revealing the information but want to persuade them that we know the secret or our statement is true
Now there are 2 types of Zero knowledge proofs
Suppose You have to ZKP that you are >=18 of age, without actually revealing you age. We need a third-party authority that can vouch for your age as follows
The authority says: “Thanks for the copy of the birth certificate, we see you are 21 years old. Here’s a secret number, keep it secret and safe. You will need it at later on."
“Your secret number will be hashed 22 times to make a final age hash code for you (yes, it has to be age+1 to make it all work). So there are 22 hashing steps between the secret number we gave you and this final age hash code."
“We are wrapping this up with your name, a time stamp and this final age hash code. That’s the proof kit that you will give to others.”
Now, whenever you want to prove to someone that you are over 18 then you effectively have to prove that there are more than 18 hashing steps to get from your secret number to your final age hash code.
To do this you just want to show them the last 18 hashing steps, you do this by doing the first 4 hashing steps yourself (hashing your secret number 4 times) and then giving them the result; the 4th hash.
They then hash this 18 times and (because we’ve now done a total of 22 hashes on your secret number) they will end up with the final age hash code and can verify this because this is in with the proof kit.
In effect the verifier is saying; ‘Send us a value that we can hash 18 times to get a match with your final age hash code’. If you are not 18 then you won’t have 18 steps in your final age hash code and you won’t be able to give us a starting point that we can hash 18 times to get your final age hash code.
This is also a nice example 👇
Example of a good zero knowledge proof - MathOverflow
▶But there are some limitations to this interactive method:
In 1986, Fiat and Shamir invented the Fiat-Shamir heuristic and thus came into being first algorithm to create digital signatures based on interactive zero knwoledge proofs
This Fiat-Shamir heuristic can be turned into a Non Interactive ZK proofs using a Commitment Scheme and thus came into being ZK-SNARKs or Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge
To make Fiat-Shamir Heuristic stronger commitments are used. Commitment schemes are fundamental components of many cryptographic protocols. A commitment scheme allows a committer to publish a value, called the commitment, which binds them to a message (binding) without revealing it (hiding).
Pederson commitment and Polynomial commitment are two most prominent commitment schemes being used for ZK proofs
But it wasn't until around 2013 that ZK-SNARKs became practically efficient to implement and use in real world applications.
I recommend you to read this excellent article by Vitalik Buterin An approximate introduction to how zk-SNARKs are possible explaining how they can be implemented. You might not catch hold of it in a single go. Read 3-4 times and you will get chills once you understand what's going on.
▶ In post Quantum world which also seems inevitable just like AI and Web3, we would need to ensure that the cryptographic functions we choose for the ZK-SNARKs cannot be brute forced by quantum computers. That why improvements are being made to achieve post quantum security. If you want to learn more on this, you may watch this talk by ACM👇
Improved Non-Interactive Zero Knowledge with Applications to Post-Quantum Signatures
Alright now we know what ZK proofs are but what are they used for 🤔?
There are two main use cases conceptually:
A rollup is a type of scaling solution that works by executing transactions outside of Layer 1 but posting transaction data on Layer 1. This allows the rollup to scale the network and still derive its security from the Ethereum consensus
Moving computation off-chain allows for essentially processing more transactions in total as only some of the data of the rollup transactions has to fit into the Ethereum blocks
To achieve this, rollup transactions are executed on a separate chain that can even run a rollup-specific version of the EVM
The next step after executing transactions on a rollup is to batch them together and post them to the main Ethereum chain.
The whole process essentially executes transactions, takes the data, compresses it and rolls it up to the main chain in a single batch, hence the name - "a rollup"
How does Ethereum know that the posted data is valid and wasn’t submitted by a bad actor trying to benefit themselves🤔?
Each rollup deploys a set of smart contracts on Layer 1 that are responsible for processing deposits and withdrawals and verifying proofs.
Proofs are also where the main distinction between different types of rollups comes into play.
Optimistic rollups use fraud proofs. In contrast, ZK rollups use validity proofs.
In ZK rollups, every batch posted to layer 1 includes a cryptographic proof called a ZK-SNARK. The proof can be quickly verified by the layer 1 contract when the transaction batch is submitted and invalid batches can be rejected straight away.
There is a lot more to both ZK and Optimistic rollups, the methodology of their implementation, their limitations. This is just a crisp idea. There's a lot more to it.
Many projects are developing scaling solutions for ethereum based on ZK rollups. Some prominent one are dYdX, Loopring, Polygon Miden, Polygon Hermez
Let's say two companies A and B want to use blockchain as medium to operate and communicate.
A transfers asset to B. They want this to remain within themselves. Yes blockchain would bring transparency, interoperability, data security and integrity and other benefits but why would a company share their internal logistic information openly in public? Zero Knowledge Proofs are the way to go.
Let's say you want to privately transfer some money to your friend overseas but don't want officials to snoop over it. How would you do it? Zero Knowledge proofs are the way out.
There are several other sectors where ZK proofs can have profound implications such as healthcare, insurance, e-voting, identity management.
In healthcare securing DNA data, personal information, health care records, essential medical history information, drug traceability, clinical trials, healthcare supply chain, organ transplant.
In insurance to secure insurance covernotes & certificate of Insurance in digital form, personal information, vehicle information, settling claims.
Identity Management using blockchain and ZKP have profound implication. Every kyc linked application, school, college, payment apps ask for images of our IDs like driving license, passport, voter id, national id. Our sensitive personal data is literally out there and we don't even realize it. With ZKp we can secure all of these IDs and reveal only necessary information to vendors, apps and officials. In fact we can completely revamp the way these IDs are issued using zkp.
We can use ZK proofs for all of these so that whenever some information is needed, user approves it and gives required information keeping the rest of details concealed.
It was only after 2013 that ZK-SNARKs efficient enough to practical implement and get used by developers, that's why there's a lot of scope for different apps that use ZKPs to show up in future.
Zcash, launched in 2016, is the only prominent product right now that has succeeded in implementing ZK-SNARKs and provide private transaction between users.

Source: Matter Labs github repository
zk-STARK stands for zero-knowledge scalable transparent argument of knowledge, and zk-SNARK stands for zero-knowledge succinct non-interactive argument of knowledge.
Both of these zero-knowledge technologies are non-interactive by nature, meaning the code can be deployed and act autonomously.
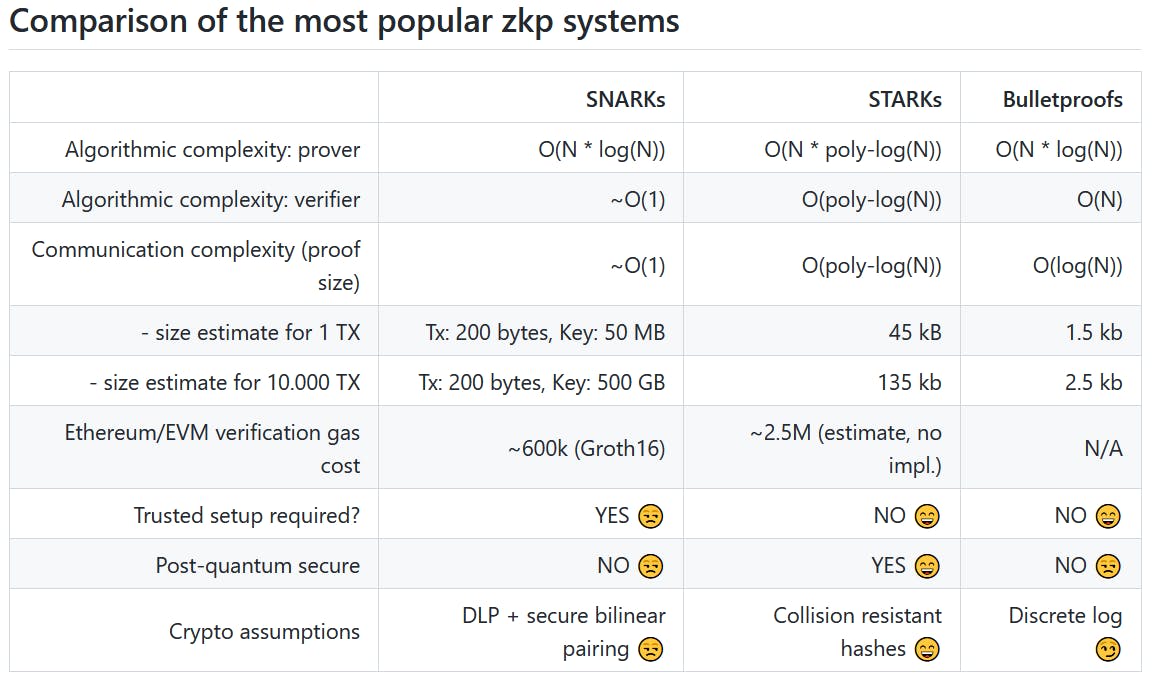
Zk-SNARKs at their base depend upon elliptic curves for their security. Elliptic curves in cryptography operate under the base assumption that finding the discrete logarithm of a random elliptic curve element with respect to a publicly known base point is infeasible. zk-SNARKs also require a trusted set up.
A trusted setup refers to the initial creation event of the keys that are used to create the proofs required for private transactions and the verification of those proofs
If the secrets used to create these keys in the trusted set up event are not destroyed, the secrets could be utilized to forge transactions by false verifications.
Another limitations of SNARKs,as we already know, their viability in post quantum world
👉On the other hand no trusted set-up is required to begin utilizing STARKs in a network. These are also labelled as quantum resistant. Though the proof size of STARK is much bigger than SNARK
But STARKs are still in nascent stage and there is not much support for developers, so there is still few years' time before we can see a ZK-STARK based product.
That's the end of it. This was small introduction to things that are being done with ZK proofs in Web3 world
所以你听说过,ZK 证明或零知识证明。但是为什么突然有嗡嗡声?它是什么?什么是 zk-rollups?什么是 ZK-SNARK?您的所有问题都会得到解答,所以请紧紧抓住并继续前进!
一种方法,一方(证明者)可以在不透露任何实际信息的情况下证明它知道秘密或对另一方(验证者)的陈述是真实的。
“零知识”一词本身证明了一个事实,即没有透露任何信息,但第二方(验证者)有理由相信第一方(证明者)知道秘密或他们的陈述是真实的。
那么为什么我们需要零知识证明呢?当我们不相信某人会透露信息但想说服他们我们知道秘密或我们的陈述是真实的
现在有两种零知识证明
假设您必须 ZKP 证明您的年龄 >=18,但实际上并未透露您的年龄。我们需要一个第三方机构,可以证明您的年龄如下
当局说:“感谢您提供出生证明的副本,我们看到您已经 21 岁了。这是一个秘密号码,请妥善保管。以后你会需要的。”
“您的密码将被哈希 22 次,为您生成最终的年龄哈希码(是的,它必须是 age+1 才能使其正常工作)。所以在我们给你的密码和这个最终的年龄哈希码之间有 22 个哈希步骤。”
“我们用你的名字、时间戳和这个最终的年龄哈希码来结束这件事。那是你会给别人的证明工具包。”
现在,每当您想向某人证明您已超过 18 岁时,您就必须有效地证明从您的密码到您的最终年龄哈希码有超过 18 个哈希步骤。
为此,您只想向他们展示最后 18 个散列步骤,您可以自己执行前 4 个散列步骤(将您的密码散列 4 次),然后给他们结果;第 4 个哈希。
然后他们对此进行 18 次哈希处理(因为我们现在已经对您的密码进行了总共 22 次哈希处理)他们最终会得到最终的年龄哈希码,并且可以验证这一点,因为这在证明工具包中。
实际上,验证者是在说;'向我们发送一个值,我们可以对其进行 18 次哈希运算,以匹配您的最终年龄哈希码'。如果您不是 18 岁,那么您的最终年龄哈希码将没有 18 个步骤,您将无法给我们一个起点,我们可以哈希 18 次以获得您的最终年龄哈希码。
这也是一个很好的例子👇
▶但是这种交互方式有一些限制:
1986 年,Fiat 和 Shamir 发明了 Fiat-Shamir 启发式算法,从而成为第一个基于交互式零知识证明创建数字签名的算法
这种 Fiat-Shamir 启发式可以使用承诺方案变成非交互式 ZK 证明,从而形成 ZK-SNARK 或零知识简洁非交互式知识论证
为了使 Fiat-Shamir Heuristic 更强大的承诺被使用。承诺方案是许多密码协议的基本组成部分。承诺方案允许提交者发布一个值,称为承诺,将它们绑定到消息(绑定)而不显示(隐藏)它。
Pederson 承诺和多项式承诺是用于 ZK 证明的两个最突出的承诺方案
但直到 2013 年左右,ZK-SNARK 才真正有效地在实际应用中实施和使用。
我建议您阅读 Vitalik Buterin 撰写的这篇出色的文章,简要 介绍 zk-SNARK 是如何实现的,并解释了它们是如何实现的。你可能不会一口气抓住它。阅读 3-4 遍,一旦你明白发生了什么,你就会感到不寒而栗。
▶ 在像 AI 和 Web3 一样似乎不可避免的后量子世界中,我们需要确保我们为 ZK-SNARK 选择的加密函数不会被量子计算机暴力破解。这就是为什么要进行改进以实现后量子安全性。如果你想了解更多,可以观看 ACM 的这个演讲👇
好吧,现在我们知道 ZK 证明是什么,但它们有什么用途🤔?
从概念上讲,有两个主要用例:
汇总是一种扩展解决方案,通过在第 1 层之外执行事务但在第 1 层发布交易数据来工作。这允许汇总扩展网络并仍然从以太坊共识中获得其安全性
将计算移出链下基本上可以处理更多的交易,因为只有一些汇总交易的数据必须适合以太坊区块
[](data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB3aWR0aD0iMjAwIiBoZWlnaHQ9IjIwMCIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB2ZXJzaW9uPSIxLjEiLz4=)
·
·
8 min read